Technical Scheme for Underground Pipeline Detection (Part 1) - Ground Penetrating Radar
1、 Geological radar method testing

(1) Basic principles
Ground Penetrating Radar is an instrument for detecting underground objects using high-frequency electromagnetic waves. It mainly uses one antenna to emit high-frequency broadband electromagnetic waves, and another antenna to receive reflected waves from underground media interfaces. When electromagnetic waves propagate in a medium, their path, electromagnetic field strength, and waveform will vary with the electrical properties and geometric shape of the medium they pass through. Therefore, based on the travel time (also known as round-trip travel time), amplitude, and waveform data of the received waves, the distribution of underground media can be inferred
(2) Reflection coefficient of electromagnetic waves
The reflection coefficient of electromagnetic waves depends on the difference in relative dielectric constants of the media on both sides of the interface. When the electromagnetic parameters of the target object and the surrounding media differ greatly, the reflection coefficient is also large, and therefore the energy of the reflected wave is also large. The reflection coefficient is not only related to the size of the incident angle, but also to the moisture content of the medium. The larger the differences, the greater the reflection coefficient, which is the physical prerequisite for ground penetrating radar detection. During the propagation of electromagnetic waves in a medium, when encountering geological phenomena with significant changes in relative permittivity, electromagnetic waves will produce reflection and transmission phenomena. The distribution of reflected and transmitted energy is mainly related to the electromagnetic wave reflection coefficient at the interface with abnormal changes
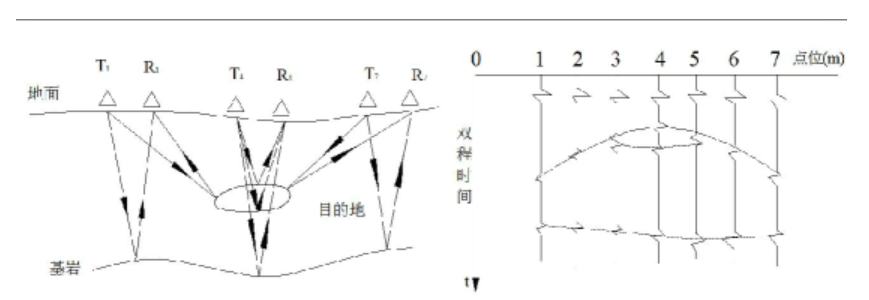
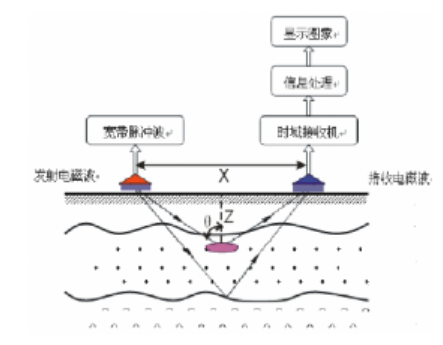
(3) Data collection and processing methods
The geological radar system consists of an integrated host, antenna, and related accessories. The specific working principle is that when the radar system uses an antenna to emit wideband high-frequency electromagnetic waves underground, the electromagnetic wave signal will undergo reflection, transmission, and refraction when it encounters a medium interface with a large dielectric difference during propagation inside the medium. The greater the difference in dielectric constant between the two media, the greater the reflected electromagnetic wave energy; After the reflected electromagnetic waves are received by the receiving antenna that moves synchronously with the transmitting antenna, the motion characteristics of the reflected electromagnetic waves are accurately recorded by the radar host, and then processed through signal technology to form a scanning image of the entire cross-section. The cross-sectional scanning image of the geological radar is shown in the figure.
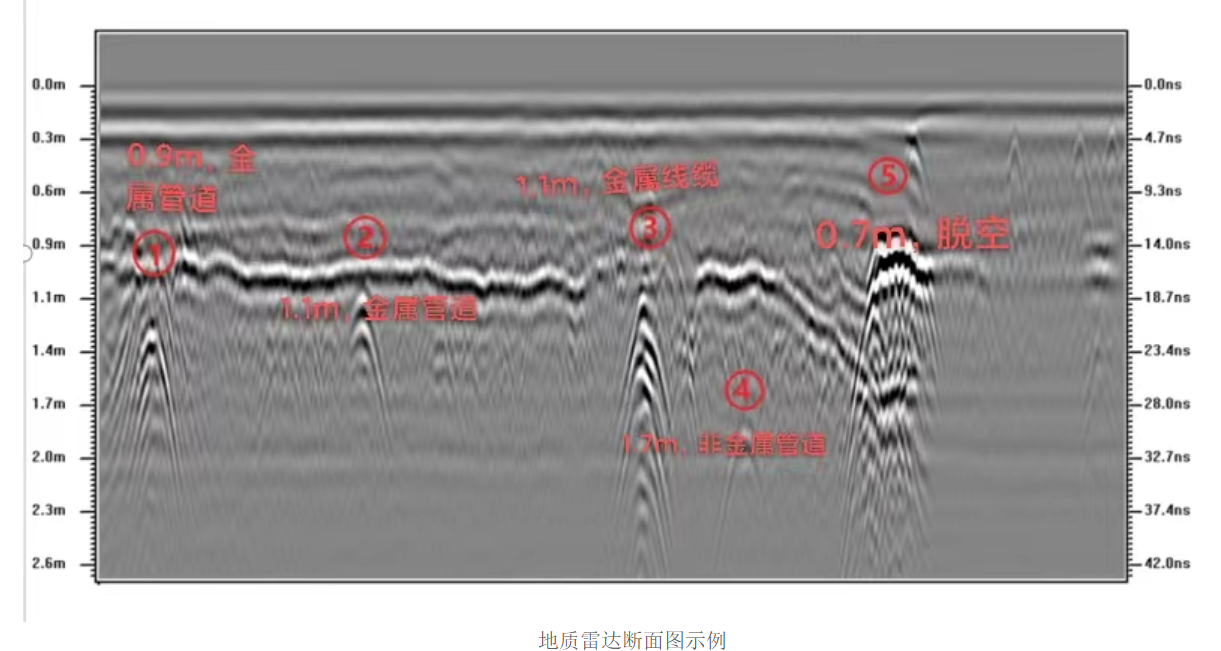
Example of Geological Radar Cross Section Map